SUMMARY: GROSS ANATOMY
Gross Anatomy – Arm Muscles 💪
There are 20 muscles that make up the forearm.
Extensor Muscles
There are twelve in number: the superficial and the deep muscles.
Superficial muscles:
They are divided into two parts:
* Lateral superficial muscle
* Posterior superficial muscle
Lateral Superficial muscles (Of forearm):
* Brachioradialis muscles
* Extensor Carpi radialis longus
* Extensor Carpi radialis brevis
Posterior Superficial muscle
* Extensor digitorum
* Extensor digiti minimi
* Extensor Carpi ulnaris
* Anconeus muscles.
There are 7 muscles that make up the Superficial region.
Deep Muscles
* Supinator muscle
* Extensor Indices
* Extensor Pollicis longus
* Extensor Pollicis Brevis
* Abductor Pollicis longus
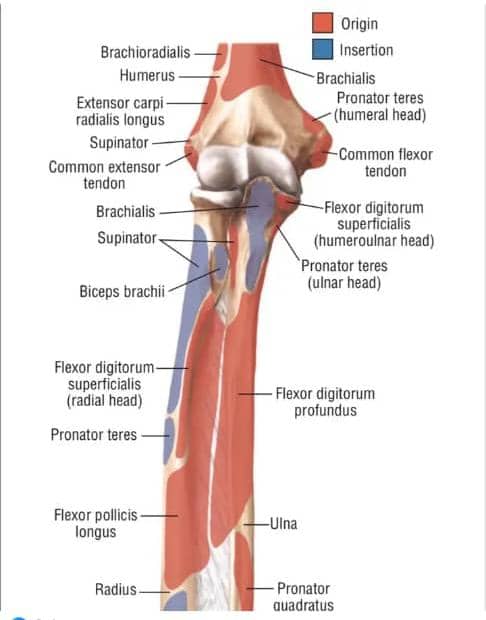
Superficial muscle: Brachioradialis muscles
* Origin: from the lateral two-third of the supracondylar ridge.
* Insertion:
* The Brachioradialis muscles shares the same origin with the ulnar nerve. It now insert into the Styloid Process of the radial bone.
* Nerve Supply:
* It is supply by the radial nerve.
* Action:
* It extend the forearm serving as the major marker of the fist.
Extensor Carpi radialis longus:
* Origin: It arises from the lower two-third
description of the forearm muscles:
… of the Supracondylar ridge. At the lateral 2/3 that is where the fleshy attachment of the Brachioradialis is located.
Extensor Carpi radialis longus: (Cont.)
* Insertion:
* It forms a flat tendon which attaches from the base of the second metacarpal bone.
* Nerve Supply:
* It is supply by the radial nerve.
* Action:
* It extends the wrist.
Extensor Carpi radialis brevis
* It originate from the Common tendon and runs beneath the Extensor Carpi radialis longus.
* Insertion:
* It forms another flat tendon and insert into the third metacarpal.
* Nerve Supply:
* It is by the radial nerve.
* Action:
* It extend the wrist joint and support in the formation of the fist. When there is damage to this muscle it will result to the ‘Tennis Elbow’.
Posterior Superficial muscles
Extensor Digitorum
* Origin: It arises from the Common extensor tendon which lies in front of the lateral Epicondyle of the Humerus.
* Insertion:
* It forms four branches, run and crosses the extensor retinaculum and insert into the proximal phalanges.
* Nerve Supply:
* It is supply by the radial nerve.
* Action:
* It helps in the expansion and extension of the digit.
Extensor Digiti minimi
* It takes its origin from the Common extensor tendon. It fuses into a tendon.
* Insertion:
* It insert into a tendon and passes beneath the extensor Retinaculum of the 5^{\text{th}} metacarpal and insert into the digiti minimi of the phalanges (little finger).
* Nerve Supply:
* It is also supply by the radial nerve.
* Action:
* Extension of the little finger is form by the action of the extensor digit minimi…
Here is the typed text from the image, continuing the notes on the forearm muscles:
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
* Origin:
* It originates from the Common extensor tendon. Common aponeurosis gives rise to the Extensor Carpi Ulnaris.
* Insertion:
* It insert into the base of the 5^{\text{th}} metacarpal.
* Nerve Supply:
* It is supply by the radial nerve.
* Action:
* It Abduct the wrist.
Anconeus muscle (Weak Extensor)
* Origin:
* It arises from the lower part of the lateral epicondyle.
* Insertion:
* It insert into the proximal part of the superior olecranon (lateral part of the lateral olecranon membrane).
* Nerve Supply:
* It is supply by the radial nerve and it… (The sentence is cut off)
* Action:
* It extends the Cubital fossa .
DEEP
Abductor Pollicis Longus
* Origin:
* It takes its origin from the oblique part of the ulna and radius close to the… (The sentence is cut off)
Would you like me to continue typing the rest of the deep muscle notes?
Abductor Pollicis Longus (Cont.)
* Insertion:
* It is inserted into the dorsal of the base and the first metacarpal bone.
* Nerve Supply:
* It is supply by the radial nerve.
* Action:
* It helps in Abduction and flexes of the wrist.
Extensor Pollicis Brevis
* Origin:
* It originates from the ulna bone.
* Insertion:
* It is inserted into the base of the distal phalanges.
* Nerve Supply:
* It is supply by the radial nerve.
* Action:
* It extends the thumb.
Extensor Pollicis Longus
* Origin:
* It originates from the radial bone.
* Insertion:
* It is inserted into the thumb.
* Nerve Supply:
* It is supply by the radial nerve.
* Action:
* It extends the terminal point of the distal phalanges of the thumb.
Extensor Indicis
* Origin:
* It originates from the ulna bone as the fibre crosses the Extensor Retinaculum into the dorsal…
* Insertion:
* The dorsal expansion of the index finger.
* Nerve Supply:
* It is supply by the radial nerve.
* Action:
* It extends and expand the index finger.
THE SUPINATOR MUSCLE
* Origin:
* It originates by the meets of two heads, divided into two by the Posterior interosseous membrane, and crosses and divides the flesh into the four part.
* The Superficial head of the Supinator muscle originates from the distal part of the lateral Epicondyle.
* Deep head arises from the Supinator Crest and the fossa of the ulna.
* Insertion:
* It is inserted into the radius between the anterior and lateral Oblique lines.
* Nerve Supply:
* It is supply by the radial nerve.
* Action:
* It separates the Forearm, especially when the forearm is extended.
CUBITAL FOSSA 📐
It is an intermuscular space that is found at the anterior region of the Elbow.
It has four parts:
Apex
Base
Content (Structures that runs in between)
Floor
Borders
The cubital fossa has two true borders: Medial border.
Lateral border.
* Medial boundary is form by the lateral border of the Pronator teres muscle.
* Lateral boundary is form by the medial border of the Brachioradialis muscles.
Apex
The Apex lies Inferior and corresponds to the joint that is formed where the Brachioradialis muscles crosses the Pronator teres muscle.
Base
The Base lies superiorly and correspond to an imaginary line which passes through the lateral Floor and Roof.
* FLOOR: The floor is form by the Brachialis muscle and Supinator muscles.
* ROOF: It is formed by the Deep facial which is straightened medially by “faceta-Fibrosus” or the “Bicipital Aponeurosis”.
Content
Structures that passes through the Cubital process, Superficial medially:
* The medial Cubital vein.
* The medial Nerve.
* The Brachial Artery and its terminal branches (Ulnar and Radial Arteries).
* The Tendon of Biceps (Biceps is the big muscle – Biceps Brachii).
* The Radial Nerve.
APPLIED ANATOMY 💡
* Most convenient side for measuring blood pressure.
* It is the only vein used for Intravenous…