SUMMARY:GROSS ANATOMY
GROSS ANATOMY 🧍🧍🧍
tubercles/tuberosity =is a small ,rounded prominence on a bone
FOSSA: is a depression or hollow , usually found in a bone .
CREST: when the bone is rough due to muscles attached to the bone it is called crest.
FORAMEN: It is a hollow depression that pierces the boneand there’s an opening to the other side.
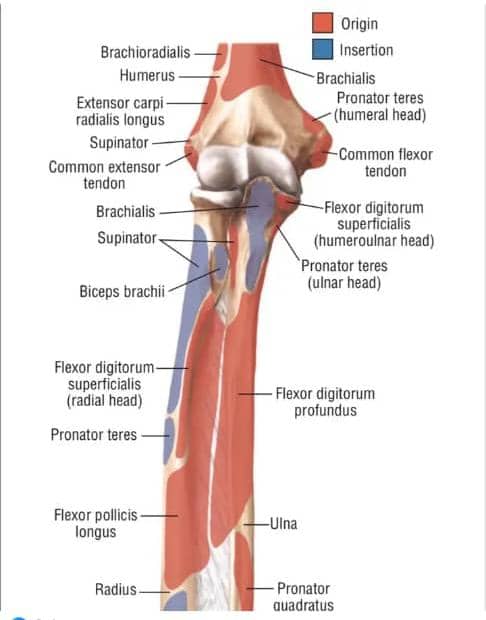
THE FOREARM HAS TWO SURFACES:-
* Anterior/Flexor surface
* Posterior extensor
INCISION is a systematic cut taken on the skin for the purpose of exposing the structure inside.
Fascia is a whitish structure that is seen after removing the skin. When the fascia is removed the next thing that is seen is the muscle, after which the bones are seen.
FLEXOR CAPRI RADIALS: Originated from the same medical epi-condyle.
INSERTION: Part of the muscle goes downward and passes beneath the flexor retinaculum. (The retinaculum looks like a rubber band and binds the muscles, carpi bones and the wrist joint together while the one infront is CALLED the FLEXOR RETINACULUM while the one behind is called the EXTENSOR RETINACULUM). It is inserted into the 2^{nd} and 3^{rd} metacarpal.
Nerve Supply: It is supplied by the median nerveof Palmaris longus: It originates from the common flexor tendon
INSERTION: It inserts into the distal part of the flexor retinaculum and the apex of the palmer aponeurosis
NERVE SUPPLY: It supplied by the median nerve
ACTION: It flexes the wrist and stretch the palmer aponeurosis
FLEXOR CAPRI ULNARIS (FCU): The flexor carpi ulnaris has an arrangement crosses through the ulna bone and the ulna nerve.
ORIGIN: It originates from the medical epicondyle of the humerus, the olecranon process of the ulna, from the medial surface of the ulna. It has three origins.
INSERTION: It inserts into the fifth metacarpal. The palm is made up of 5 bones called the metacarpal bones. The ring finger gives an approx joint with the 4^{th} metacarpal. The flexor carpi ulnaris inserts in the fifth metacarpal.
ACTION: It flexes the wrist and acts as the extensor of the elbow and helps to adduct the hand.
Flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS):
Origin: It has over 5 points of origin.
I .It originates from the common flexor tendon.
ii. From medial ligament of the elbow joint
iii. The medial border of the coronoid process
iv. From the fibrous arch connecting ulna and radius
v. From the whole line anterior oblique line of the radius or the radial bone.
approx metacarpal and passes through the palmar aponeurosis
Insertion: As the tendon passes down into the hand, it divides and insert into the five digits (the proximal phalanges).
Nerve Supply: It is supplied by the median nerve.
Action: It flexes the interphalangeal joints, it also flexes the metacarpophalangeal joints.